Often, surgery isn’t the only — or best — option for those with musculoskeletal disorders and injuries
From common athletic injuries like anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tears to joint damage from osteoarthritis, people turn to steroids, pain relievers and surgery as potential solutions for many reasons. But the truth is that a major gap for treating these conditions exists between conservative therapy and surgery. Additionally, the data doesn’t necessarily support all of the surgeries performed annually around the world — a number expected to reach around 28 million in 2022.
One out of every two adults may suffer from a musculoskeletal disorder, and many of these individuals are searching for alternative, more effective treatment methods to avoid invasive, costly procedures often accompanied by lengthy recovery times (between eight and 12 months for ACL reconstruction, for example) and post-operative pain. Because surgery doesn’t come without risks and complications, and alternatives like steroids and pain relievers aren’t long-term solutions, these aren’t always ideal options. One increasingly popular answer? Regenerative medicine.
The field of regenerative medicine includes stem cell therapy, gene therapy and therapeutic tissue engineering. It has the potential to treat, modify, reverse or cure previously intractable diseases like cancer and organ failure. And it’s already become a $27 billion global industry. But many people don’t realize that it’s used every day for the hundreds of thousands of Americans who suffer from musculoskeletal disorders, chronic pain and more. Continue reading to learn more about how regenerative medicine therapies are used, who can benefit from them and what the process is like.
For musculoskeletal disorders, is surgery worth it?
A British Medical Journal study published in 2021 found that “no strong, high-quality evidence base shows that many commonly performed elective orthopedic procedures are more effective than non-operative alternatives.” The study looked at a range of common procedures including ACL reconstruction, meniscal repair, rotator cuff repair, carpal tunnel decompression, lumbar spine decompression, total hip replacement and total knee replacement. Yet many of these surgeries are prescribed and performed every day.
It’s not uncommon for those who undergo these procedures to experience lasting pain and discomfort. In fact, the U.S. Institute of Medicine reported that 80% of patients who had surgery reported postoperative pain, and “inadequately controlled postoperative pain continues to be a widespread, unresolved healthcare problem.”

Additionally, pain management in surgery patients has negative consequences, ranging from diminished physical function and slowed recovery time to higher cost of care. John Hopkins University health economists have reported that chronic pain costs the U.S. up to $635 billion per year, and it’s one of the most common results adults seek medical care. Adults with chronic pain can miss work, are restricted in mobility and limited in their daily activities, might become dependent on opioids, and often experience anxiety and depression.
“Early postoperative pain appears to trigger persistent pain that may last for months after surgery in a substantial proportion of patients.”
Surgery and opioid dependency
One of the risks that you take when undergoing surgery is opioid dependency. Between 2005 and 2015, the number of opioids prescribed for postoperative pain increased dramatically, which has been associated with increased risk of ongoing opioid use. More than 90% of the annual 100 million surgical patients in the U.S. receive a prescription for opioids, contributing to an already serious national opioid epidemic.
While opioids do help treat pain following surgery in the short-term, the feelings of pleasure that can result from using them can lead to addiction. But when surgery hasn’t achieved the desired outcome — or patients are left in discomfort and pain — those taking them can struggle to stop.
What is regenerative medicine?
Based on the concept that stem cells — cells from which all other cells with specialized functions are generated — can rejuvenate, replace or regenerate damaged tissue in the body, regenerative medicine uses autologous (your own) healthy cells to replace damaged ones. These therapies can be a long-lasting alternative to surgery, steroids and opioids. Regenerative medicine promotes healing and treatment for a variety of injuries and conditions and while it has been used globally for decades, it’s becoming more mainstream in the U.S. As of 2021, there are currently more than 2,600 active trials for regenerative medicines.
“People who can benefit from stem cell therapies include those with spinal cord injuries, type 1 diabetes, Parkinson’s disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Alzheimer’s disease, heart disease, stroke, burns, cancer and osteoarthritis.”
Many regenerative medicine treatments involve minimally invasive outpatient procedures, and they can be used as an alternative or complimentary approach to surgery, alongside physical therapy. Patients who receive these types of procedures often experience stronger, faster recovery and healing, and don’t need long-term pain medication. Additionally, there are no side effects.
There are several kinds of regenerative medicine treatments that can help promote healing and accelerate recovery by delivering restorative cells to diseased or damaged tissue. Some of the most common include:
- Bone marrow aspirate concentration injections use bone marrow stem cells to regenerate bone, cartilage and muscle. These injections have been shown to improve pain and shoulder function in patients with partial tears of the rotator cuff tendon, among other injuries.
- Lipoaspirate injections use tissue from body fat, an abundant stem cell source, for repair and regeneration. A 19-year-old soccer player with a medical collateral ligament (MCL) tear received stem cell injections and resumed athletic activities after 122 days — compared to the average surgical recovery time of 181 days. The recovery was supported by an MRI, which demonstrated full regeneration of the damaged MCL.
- Platelet rich plasma (PRP) therapy uses blood plasma enriched with platelets to promote healing in bone and soft tissue. PRP is effective in treating knee osteoarthritis, among other musculoskeletal disorders, at all stages.
- Amniotic fluid allograft injections use amniotic fluid harvested from a donor to treat damaged tissue. These injections can help regenerate tissue in patients with chronic conditions like diabetes, heart disease and cancer since their own cells may not have the capacity to induce repair.
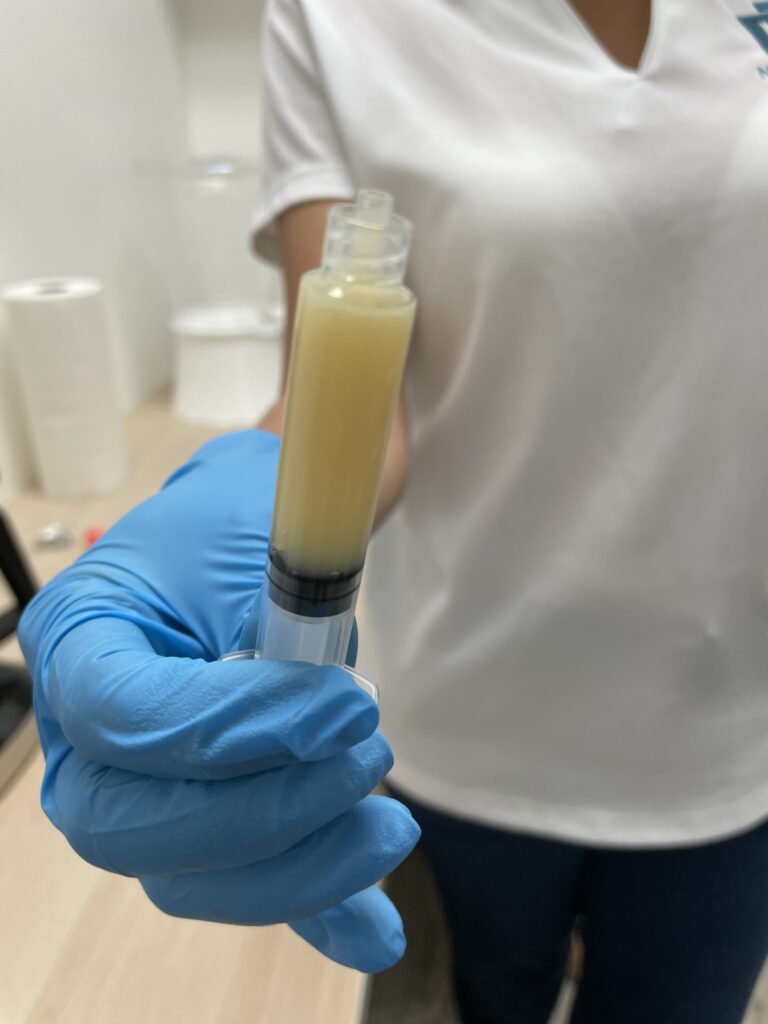
While regenerative medicine is being used to treat diseases like cancer, it’s also increasingly used for anyone with pain or discomfort from injury as well as anti-aging applications:
- Degenerative musculoskeletal disorders, e.g., osteoarthritis
- Acute and chronic injuries, athletic injuries
- Soft tissue injuries, e.g., tendonitis, tendon tears, meniscus tears, ligament tears
- Rotator cuff tears, muscle tears
- Severe sprains
- Neck and back pain
- Skin rejuvenation
Is there a more effective treatment for arthritis?
Arthritis (joint inflammation) impacts 58.5 million adults in the U.S., and is the leading cause of work disability, one of the most common chronic conditions, and a common cause of chronic pain. It’s most commonly caused by overuse of the joints, age, injury and obesity. Over time, the cartilage that cushions the ends of your bones that meet in joints wears away, causing friction, inflammation and pain. Regenerative medicine treatments using stem cells have been shown to effectively control the progression of arthritis and decrease pain and inflammation.
Achieving better outcomes through regenerative medicine
Physicians and medical researchers in the U.S. and beyond continue to study regenerative medicine treatments and their various applications, bringing more options to those looking for alternative methods to improve healing, speed up recovery time and achieve better outcomes. Harnessing the power of regenerative medicine therapy can give your body the building blocks it needs to repair tissue damage — helping you live a stronger and healthier life.
If you’re interested in learning more about regenerative medicine, contact NeoMedicine Institute today.